 Sure, there’s nothing new about saying added sugar is bad for you (regardless of your age). Your mom told you, and your doctor says so, too, but you can’t sugar-coat the truth — you love the sweet stuff. So what else is new? Well, it turns out that there is something that is both new and troubling about sugar.
Sure, there’s nothing new about saying added sugar is bad for you (regardless of your age). Your mom told you, and your doctor says so, too, but you can’t sugar-coat the truth — you love the sweet stuff. So what else is new? Well, it turns out that there is something that is both new and troubling about sugar.
A new study reported that added sugars have been found to have a profound effect in causing frailty in adults over 60. Frailty is defined by meeting three out of five of these criteria: unintentional weight loss, exhaustion, low physical activity, slow walking, and weak grip strength. The frightening consequences of frailty are an elevated vulnerability to falls, disability, and earlier death. (1)
In the study, participants were divided into three groups based on their intake of added sugars. Three years later, those participants who consumed at least 36 g sugar per day (about the amount in one 12-ounce can of soda) had more than double the risk of becoming frail over the follow-up period compared to those who consumed less than 15 g per day. Even after adjusting the group’s results for physical activity, the risk was still elevated more than two-fold in the high-sugar group. (2)
The reason? It could be sugar’s impact on muscle mass. Other research has found that high sugar intake may diminish the body’s ability to maintain muscle mass with age. (3)
And if that wasn’t enough to sour your taste for sweet, the study also found that sugars in processed foods were the most strongly associated with frailty. Given the fact that added sugar is often hidden in processed food — think tomato sauces, yogurt, ketchup and granola bars — this is concerning news for all.
Satisfy Your Sweet Tooth
Fortunately, you can still enjoy the deliciousness of naturally occurring sugars. They were not associated with an increase in frailty risk (naturally occurring sugars in this study included those in fruits and vegetables, but not fruit juices).
Instead of seeking out added sugars, try adding naturally sweet fruits and vegetables (such as carrots and sweet potatoes) to your diet. They provide valuable phytochemicals, such as flavonoids and carotenoids, and – importantly – fiber, which slows the absorption of their sugars, minimizing their glycemic effect.
The Standard American Diet: lots of sugar, very little fruit: (4)
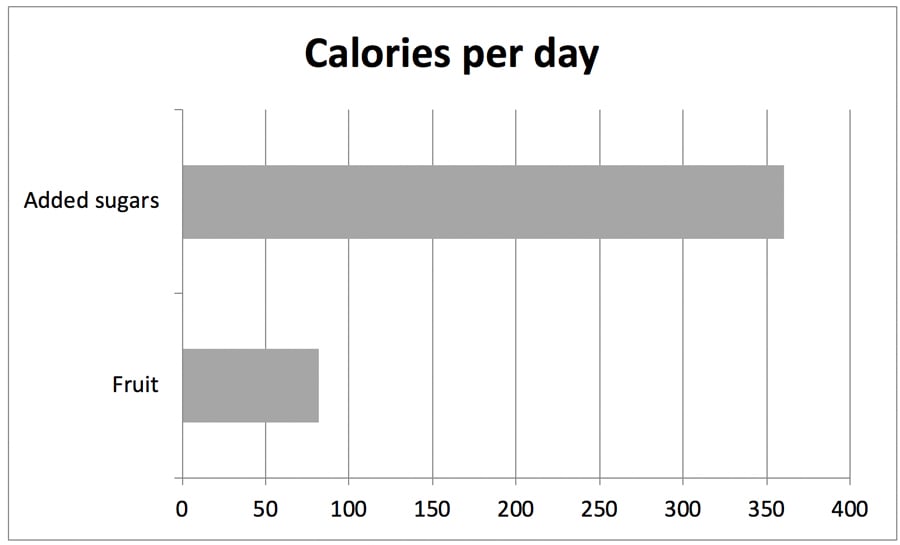
But don’t go overboard with dates and dried fruit. Avoid all sweetening agents including maple syrup and honey. Excessively sweet foods keep your taste buds accustomed to that excessive sweetness, perpetuating the desire for more sweet foods, which also promotes weight gain. When you consume overly sweetened foods regularly it makes real food such as fresh fruits not taste as spectacular. A piece of fruit for dessert or a small amount of dried fruit to sweeten a sauce or salad dressing is all you need.
Don’t Let Sugar Sour a Good Diet
A healthy diet excludes processed foods and includes a wide assortment of fruits, vegetables, beans, seeds and nuts—with their vast array of phytonutrients.
In a systematic review of many studies, researchers found a low intake of several micronutrients — including vitamin D, vitamin E, vitamin C, folate, vitamin A, vitamin B6, and carotenoids alpha-carotene, beta-carotene, and cryptoxanthin — also had links to frailty. Similarly, biomarkers of nutrient inadequacy were also linked to frailty, such as MMA (a marker of B12 deficiency), and low levels of serum carotenoids, alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E), vitamin D, and vitamin B6. (5) So you see, it is important to not only be aware of the harm caused by add sugar, but also to keep eating healthfully.
The Bottom Line
The good news? A diet with higher antioxidant capacity (like a Nutritarian diet) was associated with a lower risk of frailty.(4)
One of the most important benefit of a Nutritarian diet is that, coupled with exercise, it allows you to enjoy life in your 80s and 90s while gobbling up delicious dishes that even your sweet tooth will appreciate. This eating style not only promotes weight loss in the short term, it is designed to slow aging and maximize longevity. Here’s why:
- It provides a excellent exposure to micronutrients and antioxidants,
- It prevents age-related chronic diseases
- It helps avoid muscle loss and bone fractures,
- It optimizes immune function and brain function with aging.
A last note about protein: The loss of muscle mass associated with frailty can be due in part to undernutrition, inadequate protein in particular. The elderly may have less efficient absorption and utilization of protein, which could lead to excessively low IGF-1 levels. Older folks may require a higher and evenly distributed protein intake compared to younger and middle-aged adults to maintain muscle mass. (Read more about this topic.)
Originally printed on DrFuhrman.com. Reprinted with permission.
Joel Fuhrman, M.D. is a board-certified family physician, six-time New York Times bestselling author and internationally recognized expert on nutrition and natural healing, who specializes in preventing and reversing disease through nutritional methods. Dr. Fuhrman coined the term “Nutritarian” to describe his longevity-promoting, nutrient dense, plant-rich eating style.
For over 25 years, Dr. Fuhrman has shown that it is possible to achieve sustainable weight loss and reverse heart disease, diabetes and many other illnesses using smart nutrition. In his medical practice, and through his books and PBS television specials, he continues to bring this life-saving message to hundreds of thousands of people around the world.
References
- Xue QL. The frailty syndrome: definition and natural history. Clin Geriatr Med 2011, 27:1-15.
- Barzilay JI, Blaum C, Moore T, et al. Insulin resistance and inflammation as precursors of frailty: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Arch Intern Med 2007, 167:635-641.
- Cleasby ME, Jamieson PM, Atherton PJ. Insulin resistance and sarcopenia: mechanistic links between common co-morbidities. J Endocrinol 2016, 229:R67-81.
- Lorenzo-Lopez L, Maseda A, de Labra C, et al. Nutritional determinants of frailty in older adults: A systematic review. BMC Geriatr 2017, 17:108.


